The Australian real estate market is a cornerstone of the national economy and a significant aspect of the “Australian Dream” of homeownership. Characterized by diverse markets across its major cities and regional areas, the Australian property landscape is influenced by a complex interplay of economic factors, government policies, population growth, and lifestyle preferences. Understanding the dynamics of this market is crucial for both aspiring homeowners and seasoned investors.
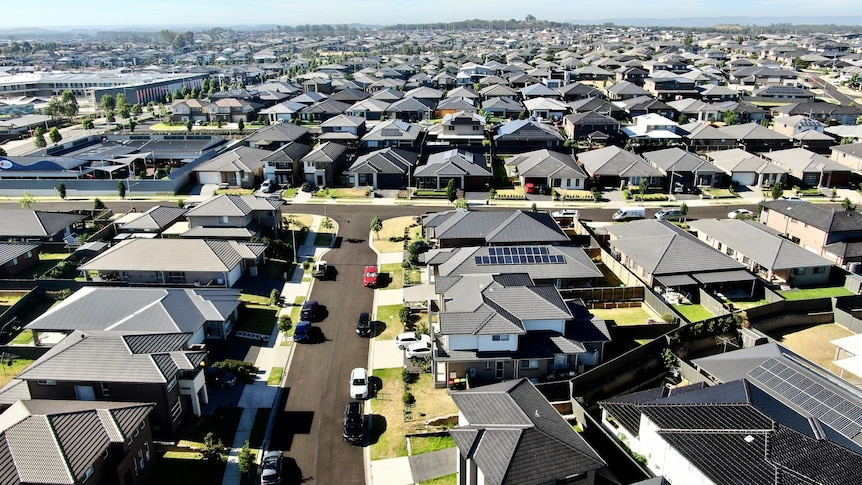
Australia’s major capital cities, particularly Sydney and Melbourne, have historically experienced high property values and strong demand, driven by factors such as robust population growth, a relatively stable economy, and international investment. However, affordability has become a significant challenge in these markets, particularly for first-home buyers. The median house prices in Sydney and Melbourne often rank among the highest in the world.
Government policies at both federal and state levels play a significant role in shaping the real estate market. Policies related to interest rates, taxation (such as capital gains tax and negative gearing), first-home buyer grants, and stamp duty can have a substantial impact on market activity and affordability. Regulatory bodies oversee the real estate industry, ensuring fair practices and consumer protection.
Population growth, driven by both natural increase and immigration, is a key factor influencing demand in many Australian property markets, particularly in major urban centers. The need for housing to accommodate a growing population puts upward pressure on prices and rental rates.
Lifestyle preferences also play a significant role in shaping demand. Coastal areas and inner-city suburbs with good amenities and transport links often command higher prices. The desire for larger family homes with outdoor space can also influence market trends, particularly in outer suburban areas.
The Australian rental market is a substantial part of the overall housing landscape, providing accommodation for those who are not yet able or do not wish to own property. Rental yields and vacancy rates vary significantly across different cities and regions, influenced by factors such as supply and demand, economic conditions, and proximity to employment and amenities.
Regional real estate markets in Australia can differ significantly from those in the major cities. Factors such as resource booms, agricultural conditions, and lifestyle attractions can drive price fluctuations in regional areas. Some regional centers offer more affordable housing options compared to capital cities, attracting buyers seeking a different pace of life or investment opportunities.
The role of real estate agents is crucial in facilitating property transactions in Australia. Agents act as intermediaries between buyers and sellers or landlords and tenants, providing market knowledge, negotiation skills, and guidance through the legal processes involved in property transactions. Licensing and regulation of real estate agents vary across states and territories.
Technological advancements are increasingly impacting the real estate market. Online property portals have become the primary way for buyers and renters to search for properties. Virtual tours, digital contracts, and online auction platforms are also becoming more common, streamlining the property transaction process.
Investment in real estate is a popular strategy in Australia, with many individuals and institutions viewing property as a long-term asset. Investment decisions are influenced by factors such as rental yields, capital growth potential, and tax implications. The prevalence of negative gearing, a tax strategy that allows investors to deduct losses from their taxable income, has historically influenced investment activity in the Australian property market.
Market cycles are a natural part of the real estate landscape, with periods of price growth followed by periods of stabilization or decline. These cycles are influenced by broader economic conditions, interest rate movements, and changes in supply and demand. Understanding market cycles is crucial for making informed property decisions.
In conclusion, the Australian real estate market is a dynamic and complex environment influenced by a wide range of economic, social, and policy factors. While the dream of homeownership remains strong, affordability challenges persist in major cities. Population growth, lifestyle preferences, government policies, and technological advancements continue to shape market trends. Understanding these dynamics is essential for navigating the Australian property landscape, whether you are a first-home buyer, a seasoned investor, or simply interested in the forces that shape the places where Australians live and work.
External Reference: CoreLogic is a leading provider of property data and analytics in Australia, offering valuable insights into market trends and property values. (https://www.corelogic.com.au/)